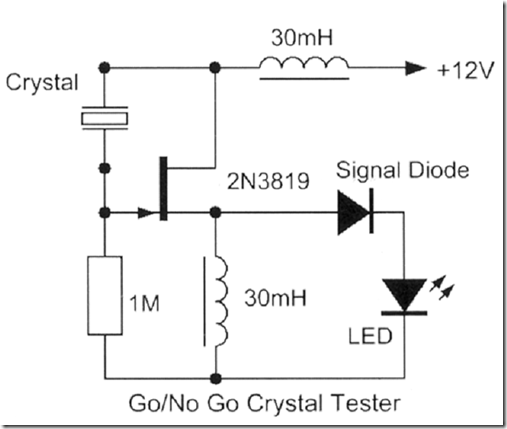
This circuit will test crystals from 1MHz to 30MHz. When the crystal oscillates, the output will pass through the 1n capacitor to the two diodes. These will charge the 4n7 and turn on the second transistor. This will cause the LED to illuminate.
This site provides schematics of various radio projects that you can experiment yourself.
Thursday, 3 March 2011
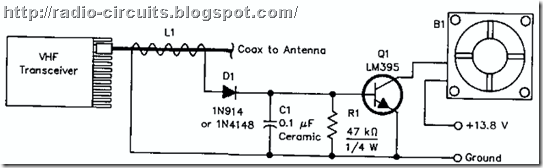
Simple circuit helps high-power VHF transceivers cool themselves
Some compact, high-power VHF transceivers get very hot when transmitting and can benefit from forced-air cooling. The simple circuit shown in Fig helps such radios cool themselves. It senses RF leakage from coaxial cable and turns on a cooling fan whenever the radio is transmitting.
Inductor Ll consists of 10 turns of insulated hookup wire-H2O to 24-wrapped tightly around the coax and taped into place. You need not alter the coax in any way. (Although my test circuit worked well with 10turns, your version may work better with more or less turns. You can optimize Ll by connecting a voltmeter across Rl and adjusting Ll for a peak read ing while transmitting.) Dl rectifies the signal. Cl filters the resulting de, which is applied to Ql's base to turn QI on. RI keeps QI turned off during no-drive periods by pulling Ql's base to ground.
The circuit has other uses. For instance, it could drive a TRANSMITTER ON indicator to warn you that your mobile mike is jammed between your car's seats with its push-to-talk button held down. Or, combined with a timer, it could serve as part of a transmitter-time-out warning circuit.
Author - Jay F. Hamlin, WB6HBS
Modulation Transformer for QRP AM transmitter projects
One the stumbling block for QRP enthusiasts, interested in building AM transmitter related projects is need of modulation transformer. I have simple solution for this. You can use audio output transformer from old radio receivers.
Wayne Burdicks modified Neophyte receiver for shortwave reception
The modification described here provides coverage of 6O·meter tropical broadcasting (4750-4995 and 5005-5060 kHz), the standard-frequency-and-time allocation at 4995-5005 kHz, 49-meter international broadcasting (5950-6200 kHz) and frequencies used by the aeronautical mobile, maritime mobile and fixed services between 4520 and 6250 kHz.
Wayne Burdick put his Neophyte receiver on 15 m and modified its audio response for better CW reception as shown here. The parts associated with U1's pins 6 and 7 serve as frequency-determining and feedback elements in U1's local-oscillator subcircuit; C1,C2, RFC1 and RFC2 reduce the receiver's audio response above 1 kHz; and R1 and C3 reduce hiss by decreasing U2's response at higher audio frequencies.
T1's secondary winding consists of 26 turns of #24 enameled wire on a T~50-6 toroidal core; the primary is 2 turns of #24 enameled wire over the secondary'S pin 2 end. l1 consists of 26 turns of #24 wire on a T-SO-6 toroidal powdered-iron core; RFC1 and RFC2 are Mouser Electronics 43LJ4l0 chokes. All electrolytic capacitors are 16 V.
See Fig and Table,. C21, a 220-pF capacitor, and S2, an SPST toggle switch are new components. S2, BAND, switches C21 in parallel with the original Neophyte's ClO to select added "low-band" option.
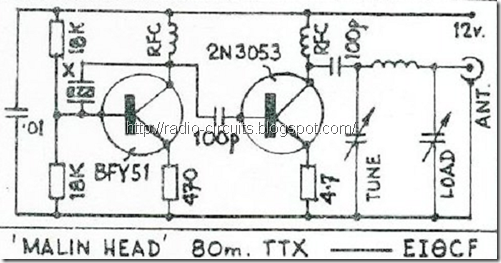
Simple QRP Transmitter
The figure shows very simple QRP transmitter for novice ham operators.The circuit misses morse key or modulation input. You can easily modified this circuit both for CW and AM operation.
Simple RF Crystal Tester
This circuit will test crystals from 1MHz to 30MHz. When the crystal oscillates, the output will pass through the 1n capacitor to the two diodes. These will charge the 4n7 and turn on the second transistor. This will cause the LED to illuminate.
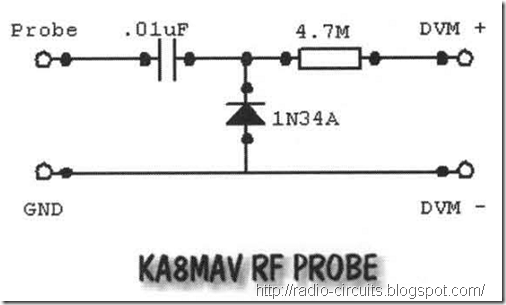
RF probe
RF probes are simple just a diode, capacitor and usually a resistor as well and are quite useful in homebrewing. The output from the junction of the diode and capacitor is a DC voltage equal to the peak voltage of the signal applied But the usual way of refemng to AC and RF voltages is by the RMS value, which is 0.707 times the peak value. We could connect a voltmeter to this point and read the peak value, then multiply by 0.707 but it's simpler to use the resistor. It forms a voltage divider in conjunction with the input impedance of the meter such that the output is approximately 0.707 of the peak,and thus the numbers on the meter correspond directly to RMS witb no conversion needed.
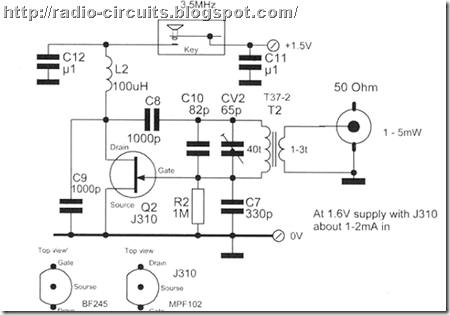
A simple low power HF CW oscillator transmitter
A simple low power HF CW oscillator transmitter is shown schematically in Fig. By using a crystal-controlled oscillator, we gain frequency accuracy and stability. This transmitter would actually work and generate a few mW of RF power at the crystal frequency.
Green Powered Ultra low power QRP Transmitter
Believe or not, the above circuit shows very low power QRP CW transmitter which emitts just 3 milliwatts. This circuit can be powered with 1.5v button cells or natural power sources like lemon,potato etc.
Simple Variable BFO for CW and SSB reception
The figure shows a simple variable beat frequency oscillator to resolve CW and SSB signals. L1 & L2 is centre tapped 300uH Inductor coil.The circuit runs on 1.5 v.
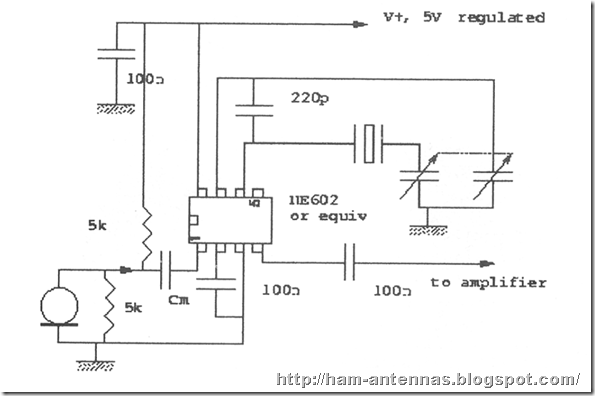
Active Antenna using Operational Amplifier
The circuit shows active antenna using operational amplifier OP27 or LT1252. Both are having cut-off frequency of 100mhz.
Active Reverse Polarity Protection For your Rig
This Circuit provides simple reverse polarity protection for your rig. It improves your battery life since power droploss and voltage drop are less.
Some Rules on VFO Stability
Shortened list of VFO rules:
1) Keep RF power output to a minimum. (Depend on subsequent stages to build it up--WA8MCQ)
2) Feedback to maintain oscillation should he minimized.
3) Shield the Ls and C's of the VFO tank components.
4) DC supply instability and ripple should he minimized.
5) Decouple DC coming into the oscillator carefully.
6) Lightly couple the oscillator to the buffer.
7) The huffer stage should have constantinput impedance.
8) The huffer stage should have low reverse gain.
9) The fT specification of the oscillator device should be at least 20 times the operating frequency.
10) There should he a means of stabilizing oscillator amplitude.
11) Use low-temperature coefficient, low loss caps such as NPO, silver-mica, polystyrene.
12) Use parallel caps where RF current is high.
13) Use good quality air variables: brass plates, double-end bearings.
14) Use a solid air-wound coil on a ceramic, glass or plastic form.
15) Use Q-dope on home-made coils.
16) For coils with slugs, use low-temperature coefficient iron-powder material.
17) Keep slug penetration into the coil to a minimum.
18) Inductors and capacitors in the VFO tank shouldn't encounter any airflow.
19) Keep stray inductance and capacitance low: short lead length, wide ground return path (big ground plane), no
double-sided PC board construction.
20) Reduce mechanical vibration: mount all critical components securely; wiring should be solid, heavy gauge wire.
Low-cost DIY Short-wave transmitter
This low-cost short-wave transmitter is tunable from 10 to 15 MHz with the help of ½J gang condenser VC1, which determines the carrier frequency of the transmitter in conjunction with inductor L1. The frequency trimming can be done with VC2. The carrier is amplified by transistor T4 and coupled to RF amplifier transistor T1 (BD677) through transformerX1*.
The transmitter does not use any modulator transformer. The audio output from condenser MIC is preamplified by transistor T3 (BC548).The audio output from T3 is further amplified by transistor T2 (BD139), which modulates the RF amplifier built around transistor T1 by varying the current through it in accordance with the audio signal’s amplitude.RFC1 is used to block the carrier RF signal from transistor T2 and the power supply.
The modulated RF is coupled to the antenna via capacitor C9. For antenna, one can use a 0.5m long telescopic aerial. Details of
RF choke, inductor L1 and coupling transformer are given in the figure.
Crystal controlled AM transmitter
Sorry for spanish text in circuit.
For modulation transformer you can use audio output transformer in transistor radio receivers.
CW / AM TRANSMITTER
The circuit is almost ridiculously simple, and construction is even simpler. It is basically a single transistor oscillator with a very low output impedance, suitable for driving the base of another transitor amplifier stage.
The oscillator uses a single coil and crystal. The coil is tuned to the output frequency, which may correspond to the crystal frequency, or a harmonic, for example you my like to use:
The above table does NOT contain rules. You may have a 3.5MHz CW crystal, but there is no reason why you cannot tune the oscillator to 7MHz. It will work with the fundamental, 2nd harmonic, 3rd and 5th. The output power will reduce at higher harmonics and frequencies are chosen.
The power amplifier is quite straight-forward. The amplifier is biased as a linear amplifier with the collector load matching the 200 Ohms collector impedance to 50 Ohms with T2. L1 and L2 plus the three capacitors for an output low-pass filter.
Modulation is applied to the base of TR2. The MOD link is removed and pin 2 is varied from 0vDC to 12vDC to vary the TX output power from zero to full power. Pins 1 and 2 may therefore be coupled directly to a morse key and you have an HF bands QRP CW transmitter. The capacitor across the 10K resistor will also adjust the keying envelope. Leave it at 1n0 for radio control use, but increase it to 100nF for good morse. On the band this transmitter sounds surprisingly clean and well formed. Since the oscillator is continuously running, there is absolutely no chirp. Adjusting the tuning of T1 will adjust the frequency by a couple of KHz.
VHF AERIAL AMPLIFIER
This amplifier circuit can be used to amplify VHF television signals. The gain is between 5dB and 28dB. 300ohm twin feeder can be used for the In/Out leads.
One Transistor Transmitter for QRP operation
It is one transistor transmitter based on crystal.It uses primary of shortwave oscillator coil as tank coil. Shortwave osc coil and variable capacitor can be salvaged from old shortwave radio.
No Cost Field Strength meter
Using multimeter on AC ranges grounding the negative lead and raising positive as antenna makes simple Field strength meter.
Active antenna for shortwave reception
The active antenna is a two stage amplifier using FET followed by bipolar transistor.The FET offers high impedence to a small antenna.For TR1 you can use MPF102 or 2N3819.